Dental caries : causes and treatments
Teeth are covered by an outer layer called enamel that protects the dentin, the substance from which the tooth is made. Dental caries is the progressive destruction of tooth enamel. It occurs in children but also in adults.
Causes of dental caries
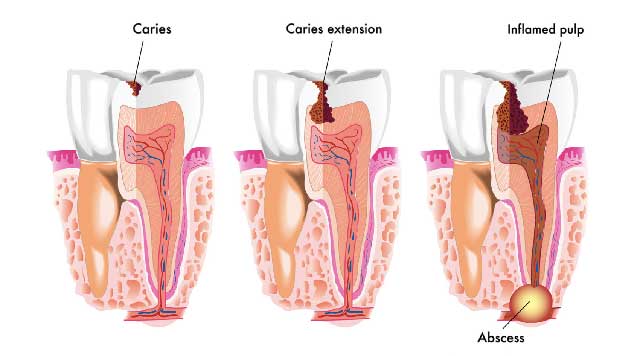
The surface of the teeth is colonized, that is occupied, by various bacteria, mainly a type of bacteria called Streptococcus mutans. These bacteria form what is known as dental plaque, which, if it is very extensive, is called tartar. If this plaque is not removed by the action of saliva or by brushing the teeth, these bacteria produce acids that demineralize and destroy the dental enamel. As a consequence, fissures and small lesions are produced, preferably in the interdental areas (between the teeth). Over time, if the damage continues, the dentin (the material of which the tooth is composed) may be affected and may extend to the dental pulp (the area where the nerves and blood vessels that innervate and nourish the tooth are located), resulting in acute pulpitis.
What symptoms does this destruction of the enamel produce?
Caries does not produce any symptoms.
When the fissure or lesion penetrates to the tooth root, pulpitis occurs. In these circumstances the tooth becomes very sensitive to hot or cold food or drinks and to palpation. The pain disappears when the painful stimulus is removed.
If germs enter the interior of the pulp and an infection occurs, irreversible damage to the tooth can be caused by the death of the pulp. In this situation, intense pain occurs, which worsens when lying down. Complete pulp death can produce intermittent or constant pain but sensitivity is lost.
How are dental caries diagnosed?
The diagnosis of caries is made by the dentist with the exploration of the teeth, usually helped with a small mirror and a sharp instrument. Sometimes it is necessary to take X-rays.
Can they be prevented?
Cavities can be prevented by daily tooth brushing and regular dental cleanings and checkups. It can also be prevented by avoiding sweet foods and/or sweets.
Dental sealants also prevent the development of cavities in children. It consists of the application of a synthetic material on the chewing surfaces of the molars, which prevents the accumulation of bacterial plaque in the deep grooves of the molars, a frequent area of dental caries. Sealing is usually performed on children shortly after eruption of the molars.
Fluoride taken by mouth or administered in toothpaste or rinses appears to reduce the risk of caries. Fluoride protects the tooth from the action of acids.
What is the treatment for cavities?
It depends on the severity of the decay :
• In very mild situations they can be reversed using fluoride alone.
• When the cavity is larger, it must be cleaned (usually using a small drill) and then filled with different substances.
• In more severe cases, the treatment consists of removing the infected tissue, sealing the exposed dentin and reconstructing the tooth structure with silver amalgam, composite resin, gold or porcelain. Sometimes if the dental caries is very large, and depending on the tooth affected, it is necessary to place a crown, a structure of different materials that covers a large area of the tooth.
• When there is irreversible damage to the root (irreversible pulpitis), it is necessary to treat the root with the extraction of the contents of the pulp and root canal, cleaning and disinfection of the area and sealing with certain material, which is called endodontics.
• In more serious cases, the tooth must be extracted.